Models¶
MF¶
Matrix Factorization (MF) used in recommender systems decomposes user-item interaction matrix 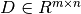 into the product of two lower dimensionality rectangular matrices
into the product of two lower dimensionality rectangular matrices 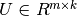 and
and 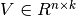 , making the product of
, making the product of 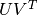 close to the real
close to the real 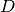 matrix as much as possible. Matrix Factorization is the mainstream algorithm based on implicit factors.
matrix as much as possible. Matrix Factorization is the mainstream algorithm based on implicit factors.
GMF¶
Generalized Matrix Factorization (GMF) is the weighted output of dot product of the embedding vectors of user and item after activation function. Let 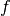 denote active function,
denote active function, 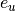 denote the embedding vector of user,
denote the embedding vector of user, 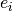 denote the embedding vector of item, $h$ denote the weights of linear function, then the result of GMF is :
denote the embedding vector of item, $h$ denote the weights of linear function, then the result of GMF is :
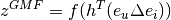
GMF usually deals with the problem of linear interaction.
MLP¶
Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) is a class of feedforward artificial neural network, consisting at least an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer. Assume a MLP model has 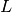 layers,
layers, 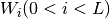 denotes the weight matrix of
denotes the weight matrix of 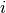 layer,
layer, 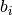 denotes the
denotes the 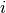 bias of MLPs,
bias of MLPs, 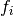 denotes the activate function of
denotes the activate function of 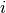 layer, then the result of MLPs is :
layer, then the result of MLPs is :
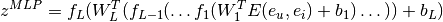
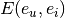 denotes the concatenation of embedding vectors of user and item. MLPs usually deals with the problem of non-linear interaction.
denotes the concatenation of embedding vectors of user and item. MLPs usually deals with the problem of non-linear interaction.
NCF¶
Neural Collaborative Filtering (MCF) is based on GMF and MLP. Let 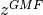 denote the result vector of GMF,
denote the result vector of GMF, 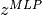 denote the result vector of MLP, then the result of NCF is :
denote the result vector of MLP, then the result of NCF is :
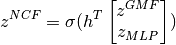
where 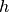 denotes the weights of NCF.
denotes the weights of NCF.
NGCF¶
Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering (NGCF) is a recommender systems framework that exploits the user-item graph structure by propagating embeddings on it, which leads to the expressive modeling of high-order connectivity in user-item graph, effectively injecting the collaborative signal into the embedding process in an explicit manner. You can find more details in the origin NGCF-paper.
LIGHT_GCN¶
LightGCN is a model containing only the most essential component in Graph Convolution Network for collaborative filtering, it learns user and item embeddings by linearly propagating them on the user-item interaction graph, and uses the weighted sum of the embeddings learned at all players as the final embedding. You can find more details in the origin LIGHT_GCN-paper.
CMN¶
Collaborative Memory Network (CMN) is a deep architecture to unify the two classes of Collaborative Filtering models capitalizing on the strengths of the global structure of latent factor model and local neighborhood-based structure in a nonlinear fashion. You can find more details in the origin CMN-paper.
Triple2Vec¶
Triple2Vec A model that learns user and item embeddings by training a Skip-gram model based on sampled triples. Triple2vec uses the Skip-gram model to recover the sampled triples (i.e. a user and two items occurring in the same basket of that user) from the users’ baskets for product representations and purchase prediction. Triple2Vec-paper.
VBCAR¶
Variational Bayesian Context-aware Representation for Grocery Recommendation (VBCAR) is a novel variational Bayesian model that learns the user and item latent vectors by leveraging basket context information from past user-item interactions. You can find more details in the origin VBCAR-paper.
NARM¶
Neural Attentive Session Based Recommendation Model (NARM) is a neural networks framework that tackle problem that not only considers the user’s sequential behavior in the current session but also emphasizing the user’s main purpose in the current session. You can find more details in the origin NARM-paper.